Describe the Structure of a Long Bone
A long bone has two main regions. Some bones in the fingers are.
Seer Training Classification Of Bones
It makes up the arm from the shoulder to the.

. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. Long bones especially the femur and tibia are. The long bones found in the arms and hands are known as.
Long bones are hard dense bones that provide strength structure and mobility. Long bones include the humerus upper arm radius forearm ulna forearm femur thigh fibula thin. Describe how bones are nourished and innervated.
This is the long central shaft. Bone tissue osseous tissue differs greatly from other tissues in the body. The diaphysis is covered protected by a fibrous.
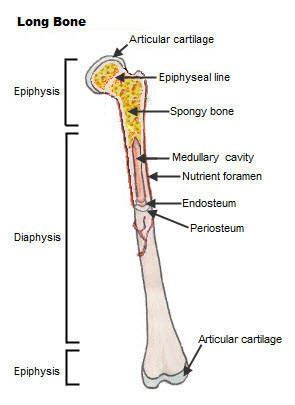
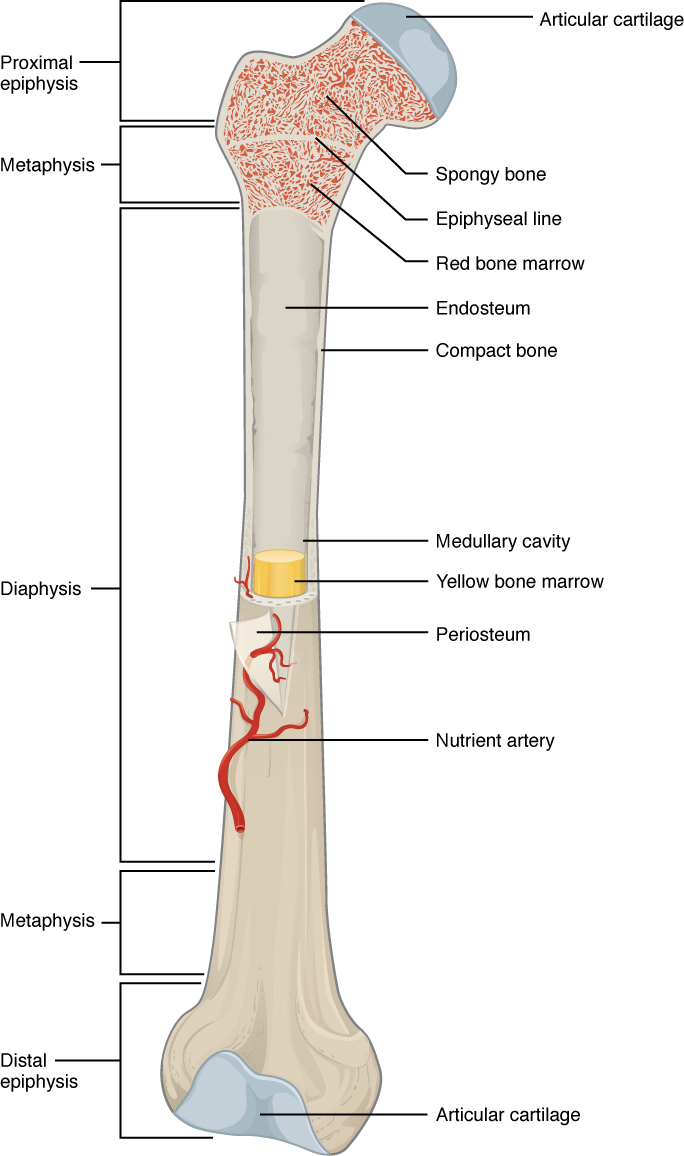
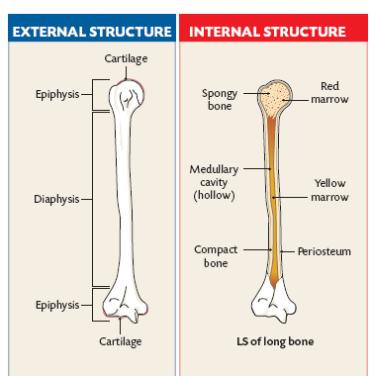
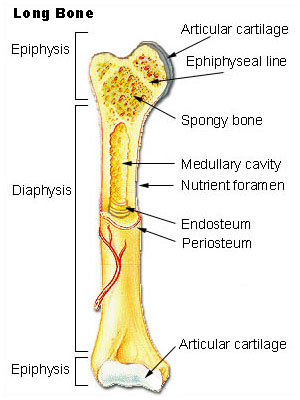
The bones typically consist of a long shaft called the diaphysis and two wider extremities on the ends called epiphyses. Gross Anatomy of Bones. The structure of a long bone allows for the best visualization of all of the parts of a bone Figure.
What is the structure of a long bone. The internal structure of a long bone is revealed by a longitudinal section. The bone contains a central medullary cavity that.
The diaphysis and the epiphysis. Compact bone tissue is composed of osteons and forms the external layer of all bones. Spongy bone tissue is composed of trabeculae and forms the inner.
The diaphysis and the epiphysis. A long bone has two parts. The typical human skeleton consists of 206 bones in adults.
The Structure of a Long Bone. These bones tend to support weight and help movement. Long bones are the most common bones found in the human body.
The diaphysis is the. Long bones are one of the five bone types that are classified by shape. The diaphysis is the hollow tubular shaft that runs between the.
The structure of a long bone consists of several sections. A long bone has two parts. A long bone has two main regions.
Long bones have a thick outside layer of compact bone and an inner medullary cavity. The diaphysis is the hollow tubular shaft that runs between the proximal and distal ends of the bone. The long bone consists of hyaline cartilage which covers the ends of the bone and stops them rubbing together as well as absorbing shock.
There are 2 humerus bones in the body one in each arm. Structure of a Long Bone - Gross Anatomy. Start studying Basic Structure of Bone - Long Bones.
They are composed mostly of compact bone and are roughly. The structure of a long bone allows for the best visualization of all of the parts of a bone Figure 1. Structure of the long bone.
A long bone is a bone that has a shaft and 2 ends and is longer than it is wide. Forms the larger rounded ends of long bones. What is the structure of a typical long bone.
A long bone has a shaft and two ends. The diaphysis and the epiphysis. Long short flat irregular and sesamoid.
The diaphysis and the epiphysis Figure 631. The long bones are those that are longer than they are wide. Spongy trabecular bone forms the internal structure of the epiphyses and the internal surface of the.
Key Skeletal System Facts. Epiphysis epiphyseal plate metaphysis diaphysis medullary cavity articular cartilage and periosteum. The thigh bone femur is a long bone.
They are one of five types of bones. The major parts of a long bone are. Diaphysis or shaft makes up the most of the bones length is composed of compact bone.
Bone is hard and many of its functions depend on that. The diaphysis is the tubular. These are mostly compacted bone with little marrow and include most of the bones in the limbs.
Bone Structure Anatomy And Physiology

Bone Structure Anatomy And Physiology I
Comments
Post a Comment